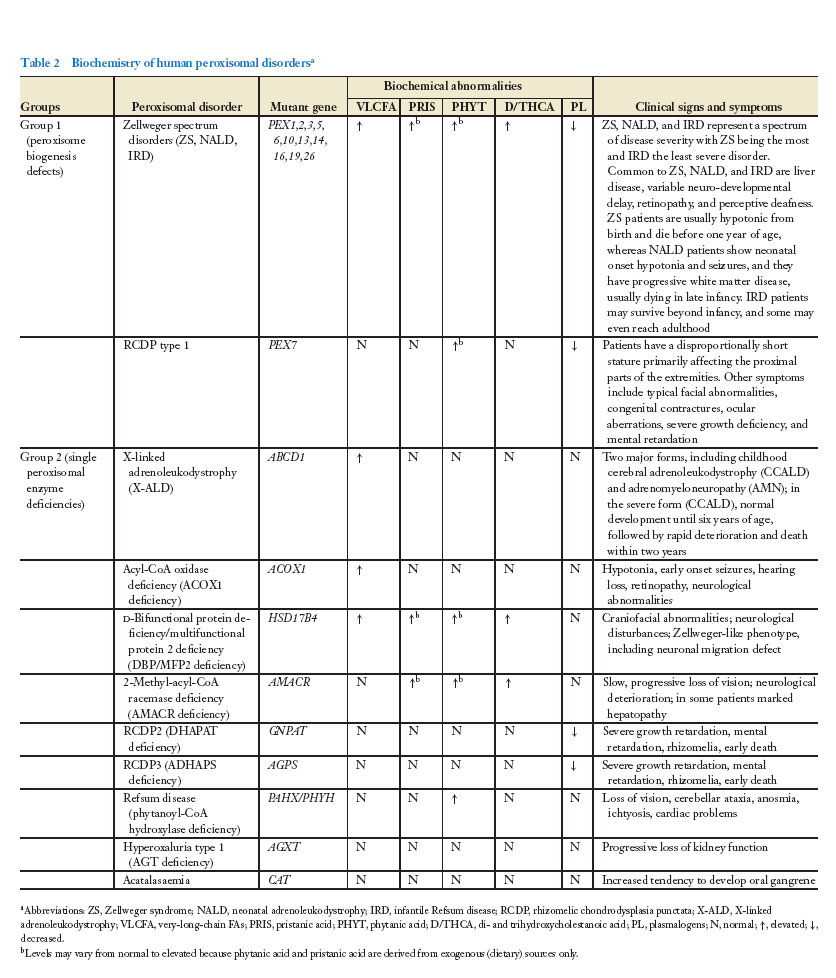
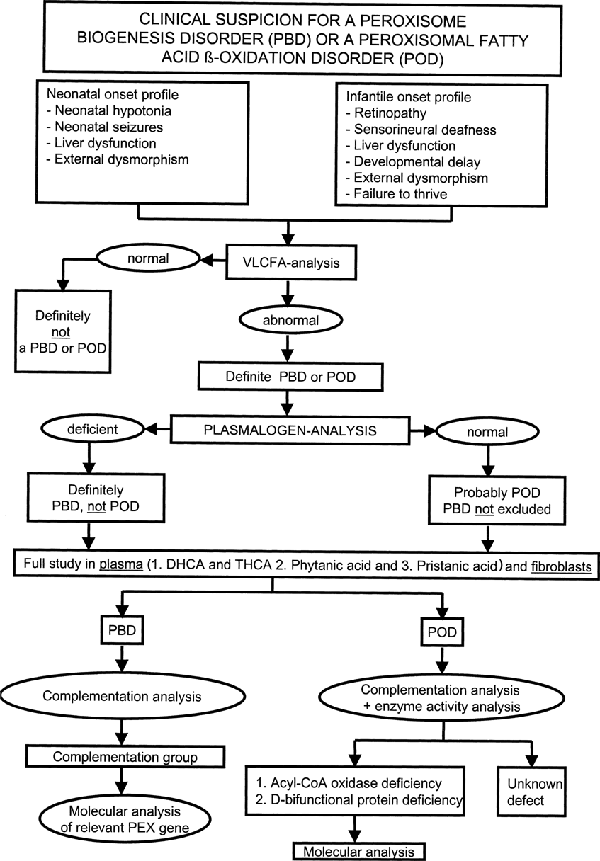
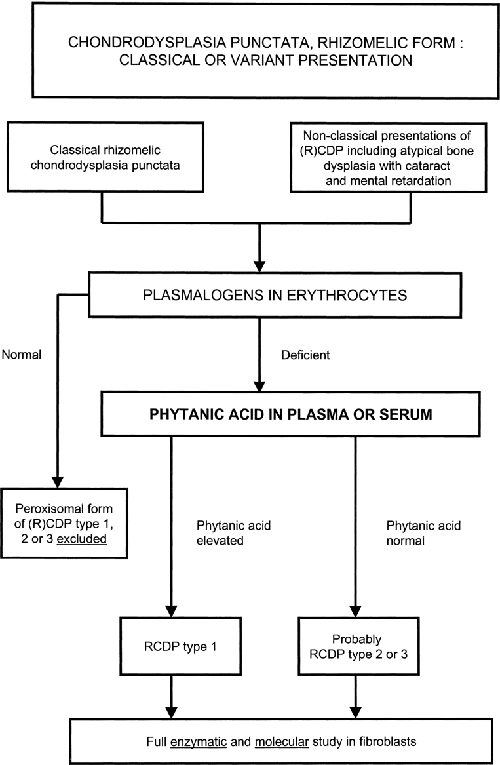
Mouse models of peroxisome biogenesis and peroxisome function.
| Disrupted gene | Deficient (enzyme) protein | Corresponding human disease | Biochemical phenotype | Clinical characteristics | ||||
| VLCFA | PRIS | PHYT | D/THCA | PL | ||||
| Pex2 | Pex2 | Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZS/NALD/IRD) | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | Intrauterine growth retardation, severe hypotonia, neonatal death, delayed neuronal migration in CNS, cerebellar abnormalities with reduced Purkinje cell development |
| Pex5 | Pex5 | Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZS/NALD/IRD) | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | Low birth weight, hypotonia, poor feeding, neuronal migration defect, neonatal death |
| Pex13 | Pex13 | Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZS/NALD/IRD) | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↓ | Low birth weight, hypotonia, poor feeding, neuronal migration defect, neonatal death |
| Pex7 | Pex7 | RCDP type 1 | N | N | ↑ | N | ↓ | Intrauterine growth retardation, severe hypotonia, delayed ossification of distal bone elements, dwarfism, delayed neuronal migration |
| Pex11α | Pex11α | — | N | N | N | N | N | No phenotypic abnormalities |
| Pex11β | Pex11β | Zellweger spectrum disorder (ZS/NALD/IRD) | N | N | N | N | N | Intrauterine growth retardation, hypotonia, developmental delay, neonatal death, impaired neuronal migration |
| Gnpat | Dhapat | RCDP type 2 | N | N | N | N | ↓ | Intrauterine growth retardation, hypotonia, male infertility, defects in eye development, cataract, optic nerve hypoplasia, prenatal death of Dhapat (−/−) embryos |
| Acox1 | Acox1 | Acyl-CoA oxidase deficiency | ↑ | N | N | N | N | Viable, but infertile; retarded postnatal growth; microvesicular steatosis; focal cell death; inflammatory reactions; liver tumors at later age (> 15 months) |
| Hsd17B4 | Dbp/Mfp2 | d-Bifunctional protein deficiency | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | N | Normal birth weight, dramatic growth retardation, up to 30% die before postnatal day 12, male infertility, no neuronal migration defect |
| Scp2 | Peroxisomal thiolase 2 (Scpx) | - | N | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | N | No phenotypic abnormalities, phytol feeding induces weight loss, neurological abnormalities, and early death within three weeks of birth |
| Abcd1 | Aldp | Adrenomyeloneuropathy | ↑ | N | N | N | N | No apparent phenotype; however, beyond age 15 months, late-onset neurological and behavioral abnormalities, axonal loss in the spinal cord, and slower nerve conduction |
| Abcd2 | Aldrp | Spinocerebellar ataxia | ↑ | N | N | N | N | No apparent phenotype; however, beyond age 15 months, areflexia ataxia, hyperactivity, slower nerve conduction, axonal loss in the spinal cord, and Purkinje cell death |
| Ehhadh | Lbf/mfp1 | - | N | N | N | N | N | No phenotypic abnormalities |
| Slc27a2 | Vlcs | - | N | N | N | N | N | No phenotypic abnormalities |
| Amacr | Amacr | AMACR deficiency | N | ↑ | N-↑ | ↑ | N | No phenotypic abnormalities, intolerance to phytol with liver disease and early death |
| mThb | Thiolase B | - | N | N | N | N | N | No phenotypic abnormalities |
| Cat | Catalase | Acatalasemia | N | N | N | N | N | No phenotypic abnormalities except for increased susceptibility to trauma-induced dysfunction of brain mitochondria |