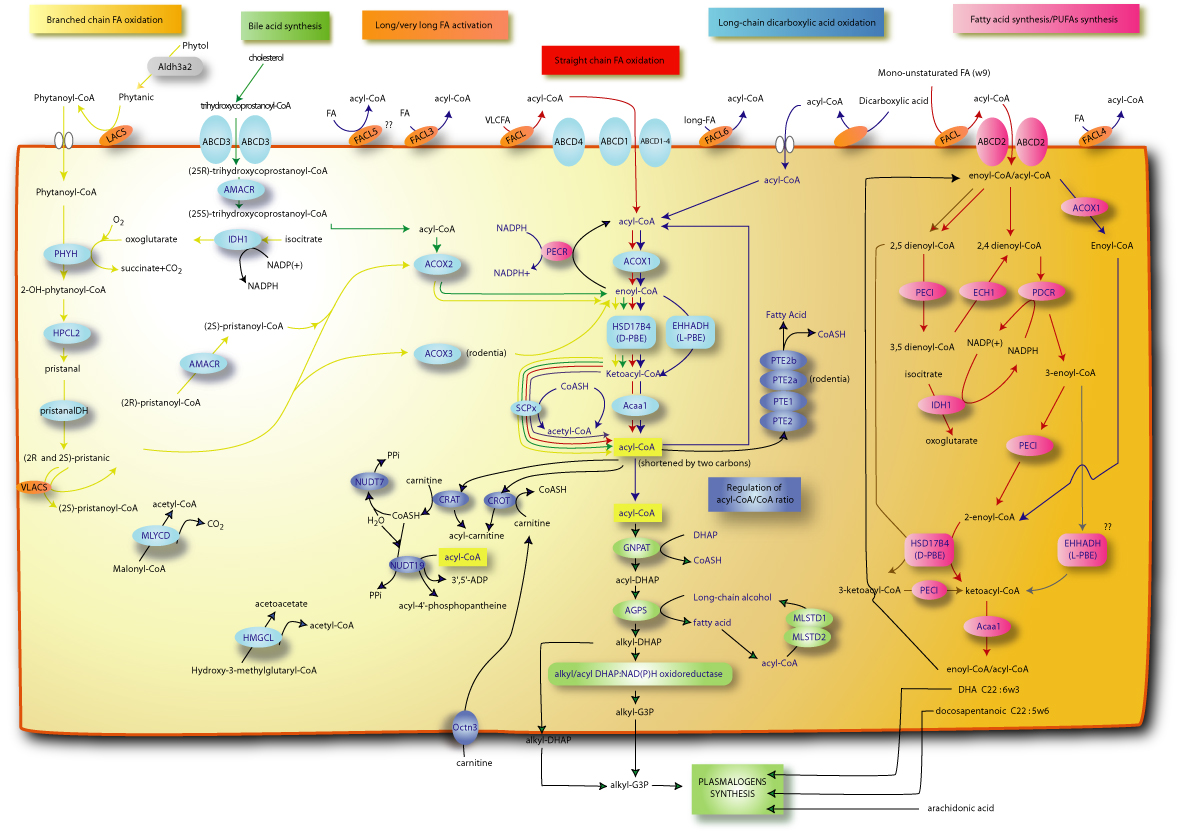
| Name : | Alpha-oxidation | ||||||||||
| Organism : | Monodelphis domestica | ||||||||||
| Description : | This function is present in vertebrates and in Caenorhabditis elegans is predicted. The alpha-oxidation removes the terminal carboxyl group as CO2 displacing the 3-methyl, in 3-methyl-branched fatty acids, to a position that allows the following beta-oxidation steps. One of the most important 3-methyl branched fatty acid is phytanic acid. Enzymes involved in the alpha-oxidation:
a) FACL1 or LACS: activates phytanic acid to phytanoyl-CoA, b) PHYH: hydroxylates the phytanoyl CoA, c) HPCL2: decarboxylates to pristanal, d) pristanalDH: dehydrogenates pristanal to pristanic, e) VLACS: activates pristanic to prystanoyl-CoA, f) IDH1: produces oxoglutarate used by PhyH.
|
||||||||||
| Gene(s) : |
| ||||||||||
| Disease(s) : | |||||||||||
| Image(s) : |
Lipid metabolism
Move your mouse pointer on the image, it will change form on clickable areas