Lipid metabolism
Move your mouse pointer on the image, it will change form on clickable areas
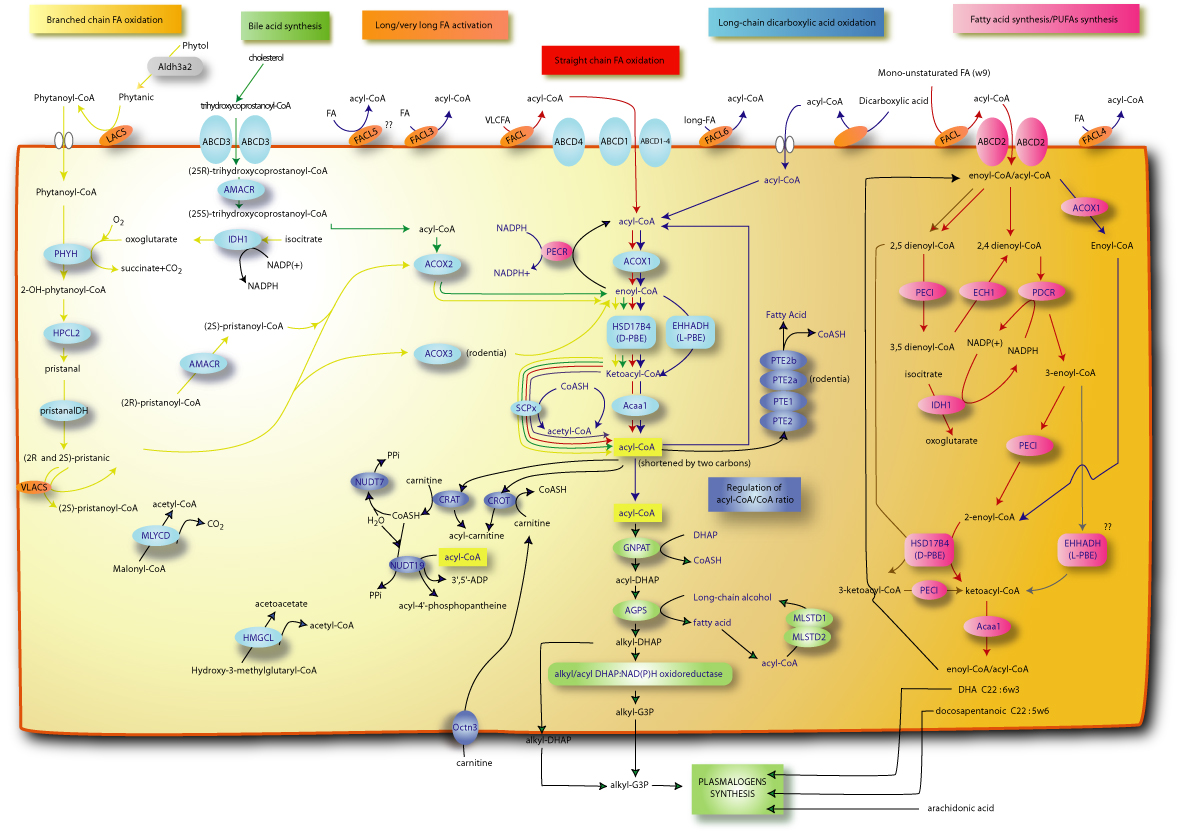
| Name : | Long-chain dicarboxylic acids oxidation | ||||||||||
| Organism : | Caenorhabditis elegans | ||||||||||
| Description : | Dicarboxylic acids are omega-oxidation products of monocarboxylic acids. In mammals, the monocarboxylic acid is omega-hydroxylated by a microsomal P450, then is alcohol and aldehyde dehydrogenated in the cytosol and, finally, is shortened in the peroxisome by the peroxisomal beta-oxidation. | ||||||||||
| Gene(s) : |
| ||||||||||
| Disease(s) : | |||||||||||
| Image(s) : |
Lipid metabolism
Move your mouse pointer on the image, it will change form on clickable areas
