| Name : | Etherlipid and plasmalogens synthesis | ||||||||
| Organism : | Ciona intestinalis | ||||||||
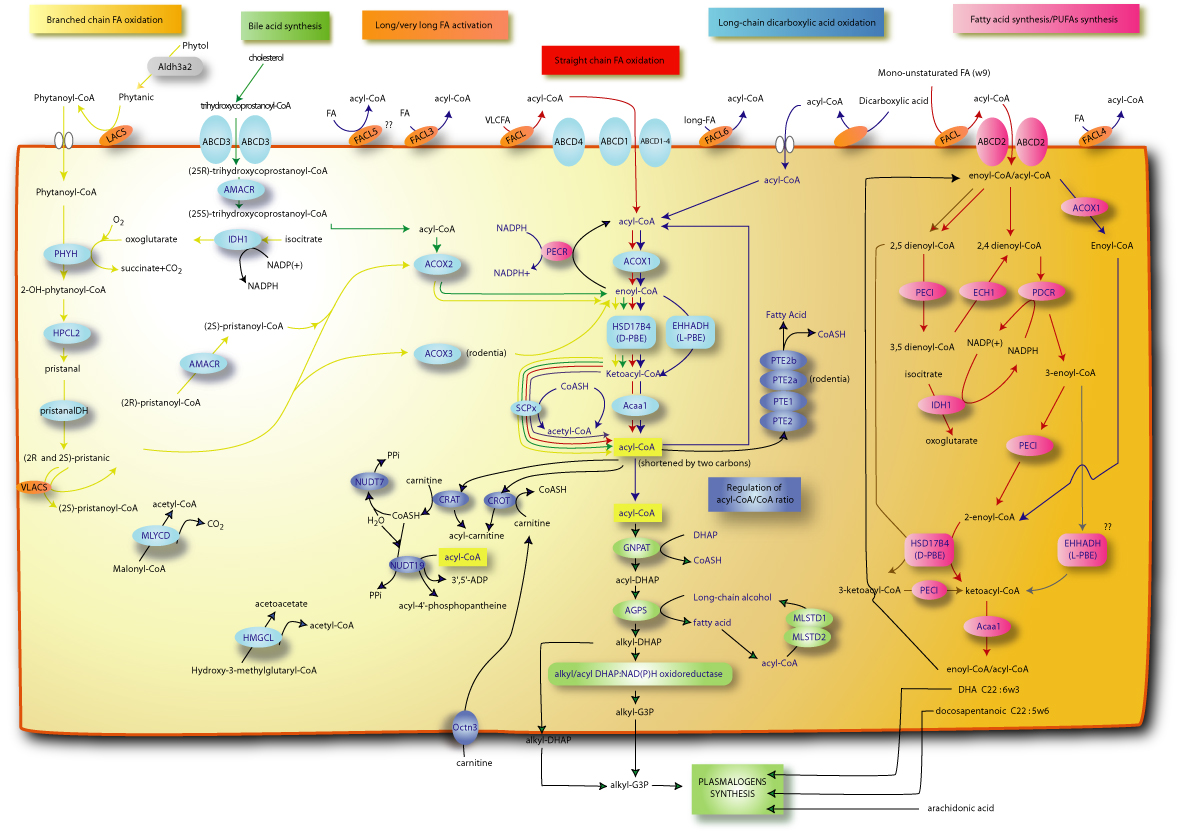
| Description : | Ether-phospholipids or plasmalogens are a special class of phospholipids characterized by a vinyl ether bond at the sn-1 position of the glycerol backbone. This pathway is widespread in peroxisomal bearing organisms except in plants and fungus. In mammals, usually at sn-1 the fatty acid sterified is a C16:0 (palmitic acid), C18:0 (stearic acid) or C18:1 (oleic acid), at sn-2 is a polyunsaturated fatty acids, such as arachidonic (AA) or docosahexaenoic (DHA) acids, and at sn-3 there is an ethanolamine or choline. The first two steps of the synthesis of plasmalogens are exclusively peroxisomal, and the following steps might occur in peroxisomes and endoplasmatic reticulum. | ||||||||
| Gene(s) : |
| ||||||||
| Disease(s) : | |||||||||
| Image(s) : |
The first two steps in plasmalogen biosynthesis take place in peroxisomes by the peroxisomal enzymes DHAP-AT and ADHAP-S. The third step may occur both in peroxisomes and in the endoplasmatic reticulum (ER), since AADHAP-R has been found in both subcellular compartments. All remaining steps occur in the ER.
Lipid metabolism
Move your mouse pointer on the image, it will change form on clickable areas